Blockchain 101
What is blockchain and how is it becoming a leading choice for information storage? A handy reckoner from Shashank Balooni
Do a Google search of the word “blockchain” and your screen will be flooded with thousands of results. A quick rundown would show that blockchain is currently being used in almost everything from financial services, supply chains to maintaining land ownership records. Blockchain has even made its way into agriculture.
Emerging economies are eagerly latching on to this new technology – Chandigarh has already started employing blockchain to maintain land ownership records. Moreover, blockchain’s highly secure network has made it the best choice when it comes to maintaining digital identities. It could make financial inclusion a reality in future.
So what exactly is blockchain and how is it becoming a leading choice for information storage?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger. Much like the ledger we use right now, it stores information. But unlike traditional ledgers the information isn’t stored at one place, the ledger is distributed between all the users.
The traditional database is more like a word doc – it is stored at one place, say in one system. The blockchain, however, could be compared to a google doc that can be worked on by different people at once (all people who have access to it).
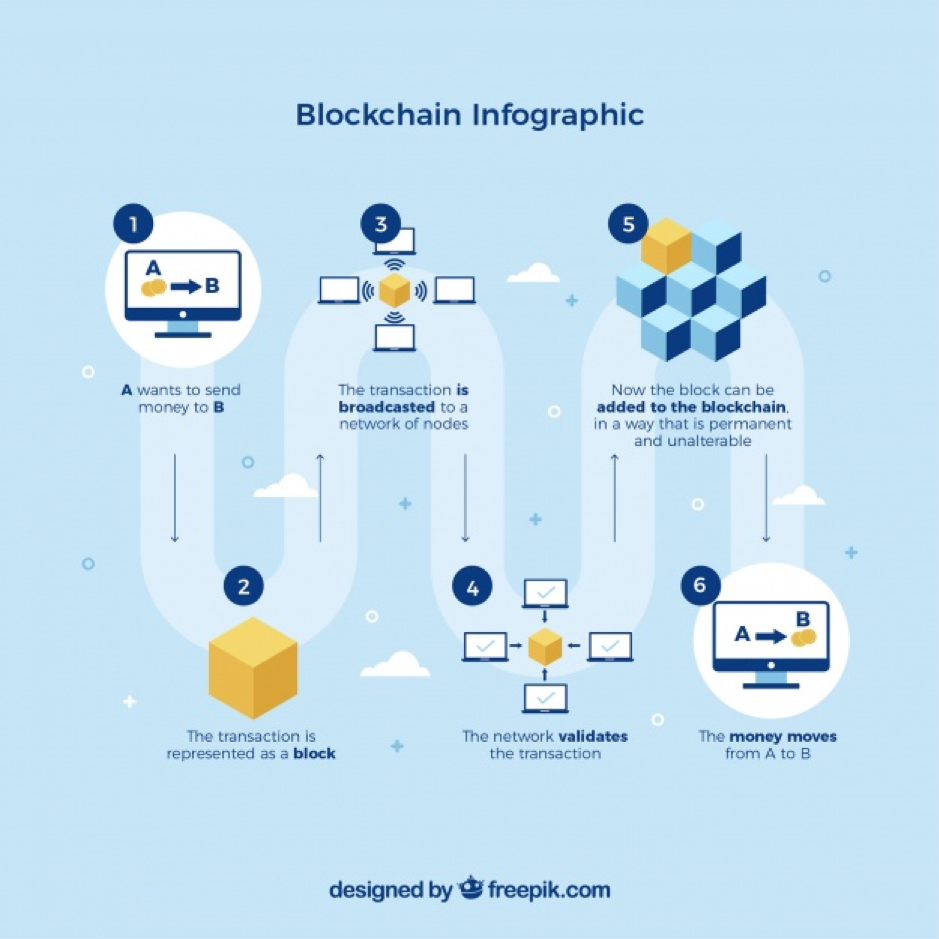
A blockchain is made up of blocks that get added once they are verified by everyone using the blockchain. So for every new batch of activity done there would be a new block added to the chain. This block would be verified by all other members of the chain. Any user cannot edit the block chain as it would not match the copy of the chain with all other users. The chain must match and then get verified! Ingenious, isn’t it? The block chain is highly secure as it is compared and checked by a copy of the chain across all users.
What this implies is that we can now remove a middle man from the equation. In land ownership records – records have always been maintained but there was no way for the buyer to verify if the documents he was receiving were authentic or not. In comes the Distributed Ledger. Now the buyer can have the assurance that the documents are verified as it can be checked on the blockchain network.
Blockchain is often confused with Bitcoins. This was bound to happen as blockchain first found it uses in the Bitcoin – the highly secure digital currency. The system was designed to remove the middlemen, in this case – banks – from the network. This is possible as now users can authenticate the transaction over the distributed ledger.
With blockchain getting adopted across different industries and disrupting them, it certainly appears as though the future of database management systems is here. One could even go so far as to say that blockchain could be the internet of tomorrow.
Do you agree? Write in to us with your views.